Hello there, I’m Luigi!
I’m a Computer Engineer and Radio Amateur (PU2SPY). Here you can find information about me and my projects. I talk about SDRs, Raspberry Pi, Machine Learning, Parallel Computing, Satellites, Python, C++, and Golang.
Thanks for visiting!
Receiving & Demodulating the Meteor Satellite
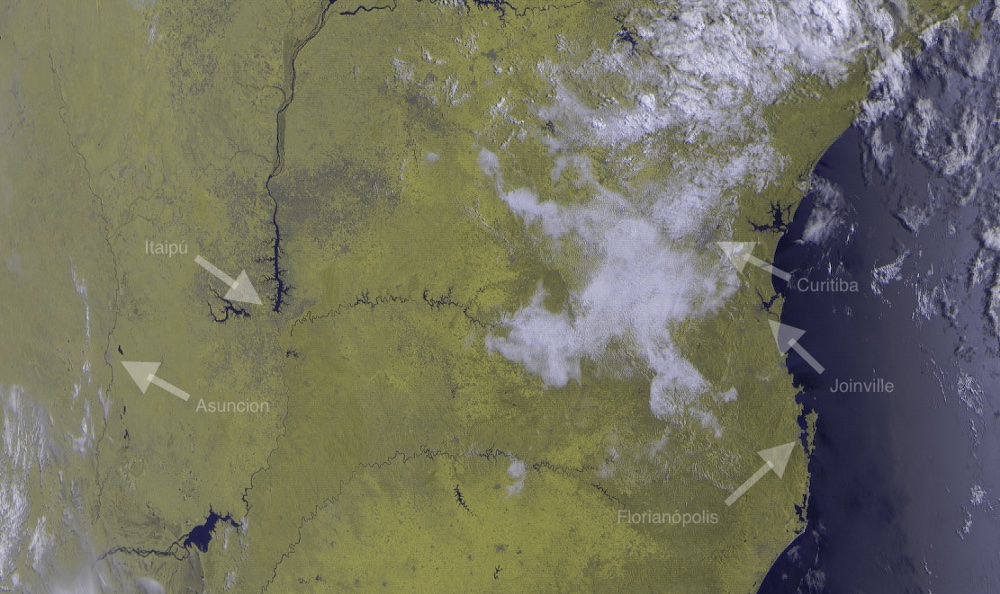
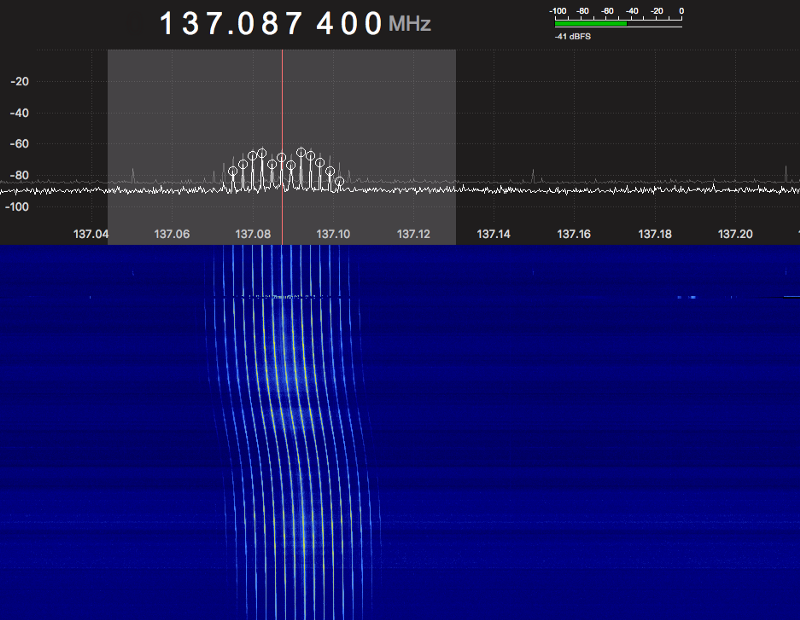
In the previous post, I talked about how I got the analog APT earth images from the NOAA sats and how I made my QFH Antenna. As I said, the APT signal is a legacy image transmission method from the 1960s that have strong drawbacks. The newest sats like Meteor-M and MetOp-A have a new protocol with digital modulation called LRPT (Low Rate Picture Transfer). Currently the single sat transmitting this protocol is the Meteor-MN2 and occasionally the Meteor-MN1.
Quadrifilar Antenna for NOAA APT Satellites
Today, America and Russia have meteorological satellites orbiting the earth every hour, as they transit thought the planet, they beam down images with a visible, mid-near infrared or infrared spectrum. With infrared is possible to identify clouds even at night as well as the temperatures of the land, sea or cloud tops.
This signal is fairly weak, so I need a big antenna. There are several types but the best choice is the QFH (QuadriFilar Helicoidal) Antenna which have the right polarization for this type of signal and it’s easy to build.
Making an Arduino Based Levitron
Me and my college group made this machine for Physics Class, so I decided to show how we made it here. The final machine can levitate a magnet smoothly for days!
What the hell is Levitron? In short, Levitron is an electromagnet controlled by a micro-controller that “levitates” a permanent rare-earth magnet by alternating the coil current. If done quickly, it creates an illusion of levitation.
How it works? This Levitron uses a Hall Effect Linear Sensor to measure the magnetic field of the magnet by creating a voltage differential that is read by the Arduino.