Trying To Run DOOM With The Raspberry Pi 4 Vulkan Driver

Vulkan is the new kid in the block for GPU accelerated tasks for Computing and Graphics. This new standard was released by the Khronos Group in 2016. When compared to OpenGL, Vulkan gives the developer more control over the hardware. This approach is widely used by other standards like DirectX 12 and Metal.
The Raspberry Pi Foundation is working with the Open-Source consultancy company called Igalia to develop Vulkan drivers for the Raspberry Pi 4 Broadcom SoC.
Monitoring GNSS Constellations with Galmon Using the LimeNET Micro Ublox-M8 Module
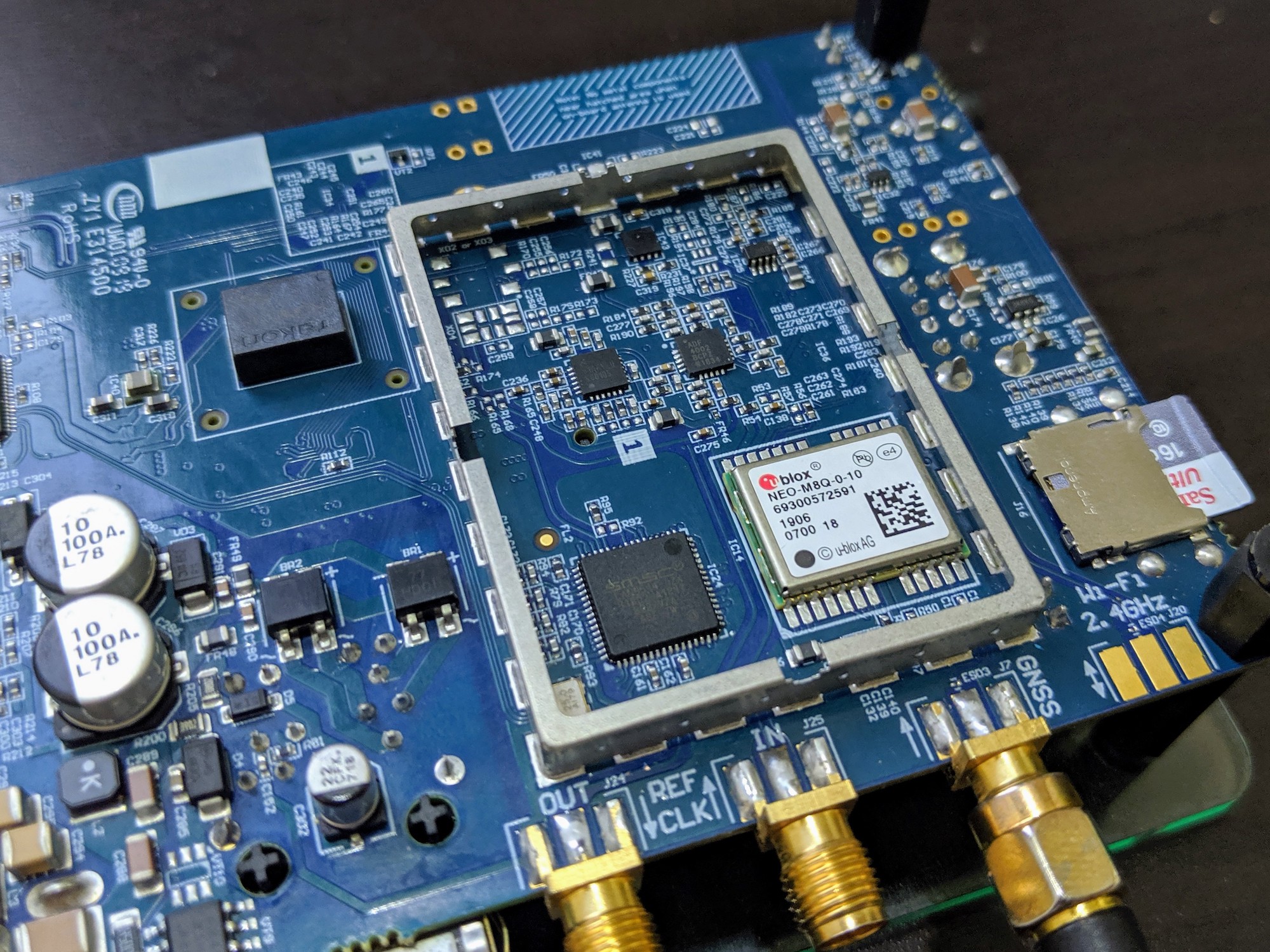
In this blog post, I will explain how I managed to get a GNSS multi-constellation monitor called Galmon working on my LimeNET Micro. The Galmon project is a crowdsourcing tool developed by @PowerDNS_Bert to monitor the health status of GNSS constellations including the GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and more notably Galileo. The project relies on volunteers to set up inexpensive stations based on the Ublox-M8 module to receive GNSS packets and send diagnostic data back to an aggregator.
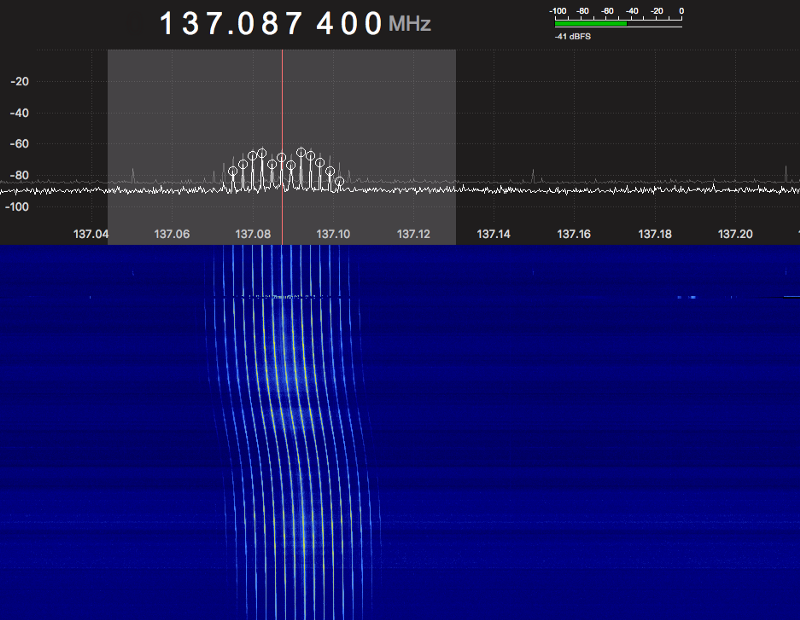
Software Defined Doppler Radar with LimeSDR Mini
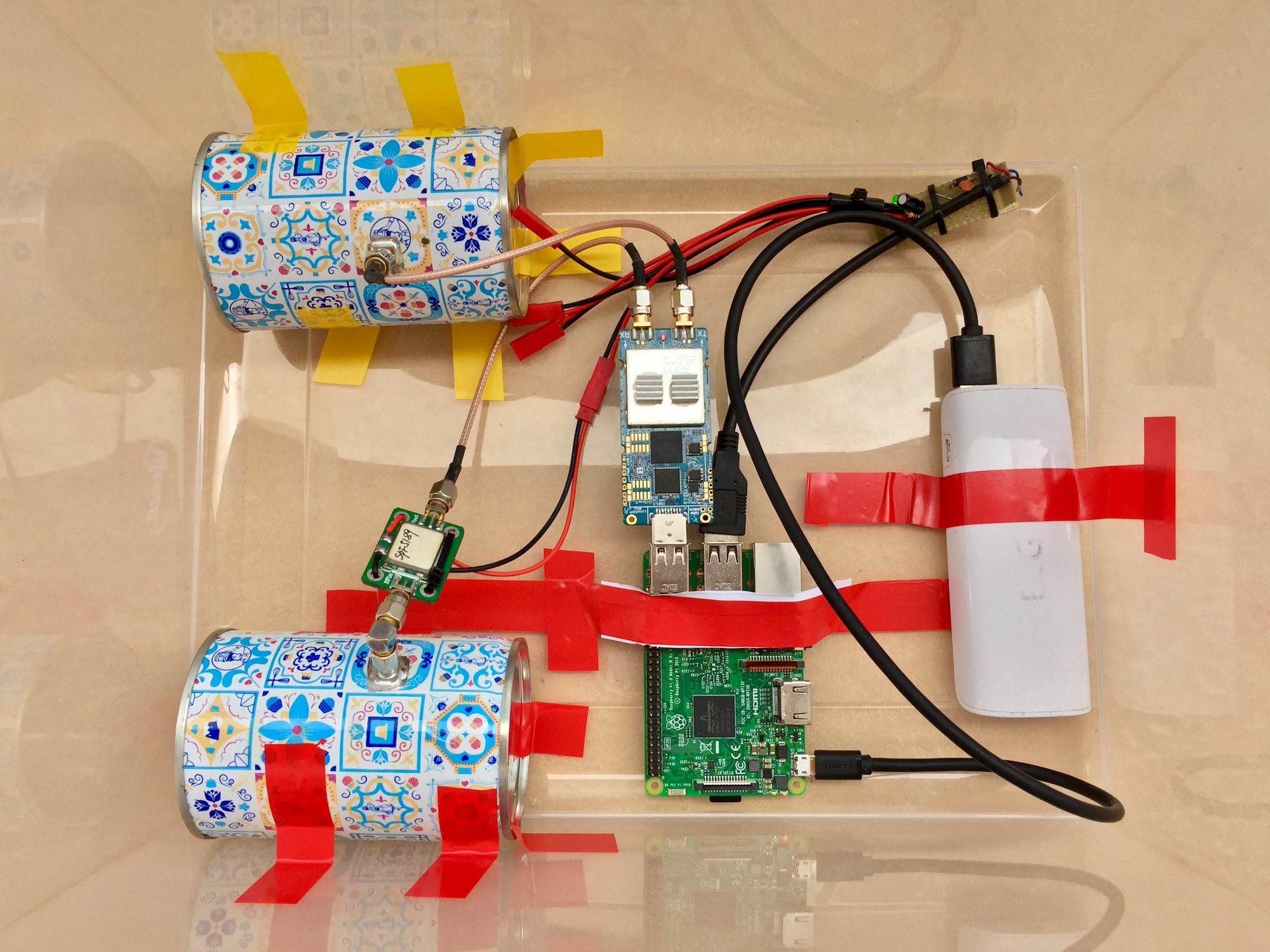
In this blog post, I’ll talk about my experiments with Software Defined Radar. This concept implies that radar systems can be simplified by abstracting analog hardware in favor of software implementations performing Digital Signal Processing inside a processor module. This is useful for aerospace applications. It lowers the complexity of the radar system consequently reducing the maintenance, weight and the probability of something misbehave in-flight.
After reading about that, I wondered if it was possible to make something similar to reduce the number of expensive analog front-end parts needed for a radar system.
Reverse Engineering GOES-16 CDA Telemetry
In this post, I’ll detail how I managed to reverse engineer the telemetry signal from GOES-16 — NOAA’s third generation geosynchronous weather satellite built by Lockheed Martin and launched into space by ULA’s Altas V rocket.
GOES-16 Telemetry Being Demodulated and Decoded. This satellite is mostly known by the HRIT signal, responsible to distribute high-resolution meteorological data to hundreds of institutions throughout the portion of the earth illuminated by the spacecraft.
Outernet Receiver with a Wifi Grid Antenna
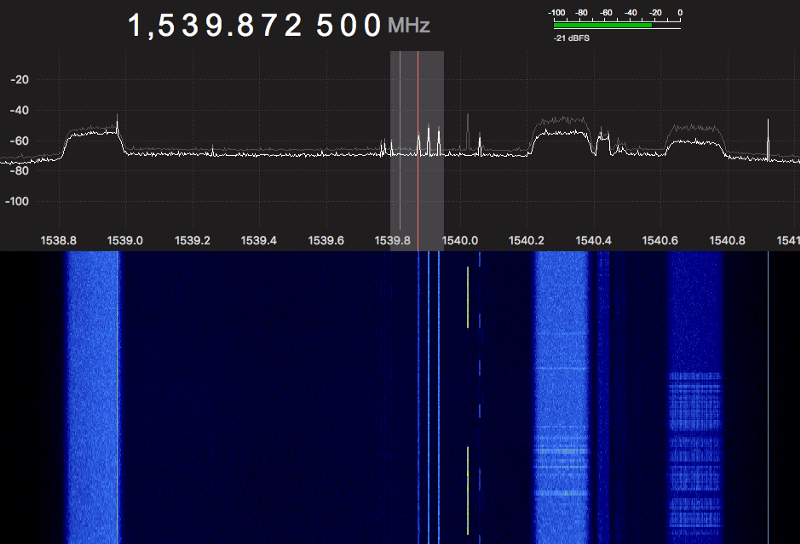
I originally bought most of this hardware for the reception of the HRIT & LRIT signals coming from the NOAA’s GOES Geostationary Satellites. Since I’m waiting for more LNAs to arrive from China, I decided to play around with my stock Wi-Fi Grid Antenna and figure out what else I can do with it.
Although this is a 2.4Ghz antenna, the L-Band is close enough for a good SNR. Thus, I can receive almost every signal on the L-Band with this stock antenna, great!
Receiving & Demodulating the Meteor Satellite
In the previous post, I talked about how I got the analog APT earth images from the NOAA sats and how I made my QFH Antenna. As I said, the APT signal is a legacy image transmission method from the 1960s that have strong drawbacks. The newest sats like Meteor-M and MetOp-A have a new protocol with digital modulation called LRPT (Low Rate Picture Transfer). Currently the single sat transmitting this protocol is the Meteor-MN2 and occasionally the Meteor-MN1.
Quadrifilar Antenna for NOAA APT Satellites
Today, America and Russia have meteorological satellites orbiting the earth every hour, as they transit thought the planet, they beam down images with a visible, mid-near infrared or infrared spectrum. With infrared is possible to identify clouds even at night as well as the temperatures of the land, sea or cloud tops.
This signal is fairly weak, so I need a big antenna. There are several types but the best choice is the QFH (QuadriFilar Helicoidal) Antenna which have the right polarization for this type of signal and it’s easy to build.
Making an Arduino Based Levitron
Me and my college group made this machine for Physics Class, so I decided to show how we made it here. The final machine can levitate a magnet smoothly for days!
What the hell is Levitron? In short, Levitron is an electromagnet controlled by a micro-controller that “levitates” a permanent rare-earth magnet by alternating the coil current. If done quickly, it creates an illusion of levitation.
How it works? This Levitron uses a Hall Effect Linear Sensor to measure the magnetic field of the magnet by creating a voltage differential that is read by the Arduino.